How to Sell Your Product
Seed Funding 101: What Founders Need to Know
February 2, 2022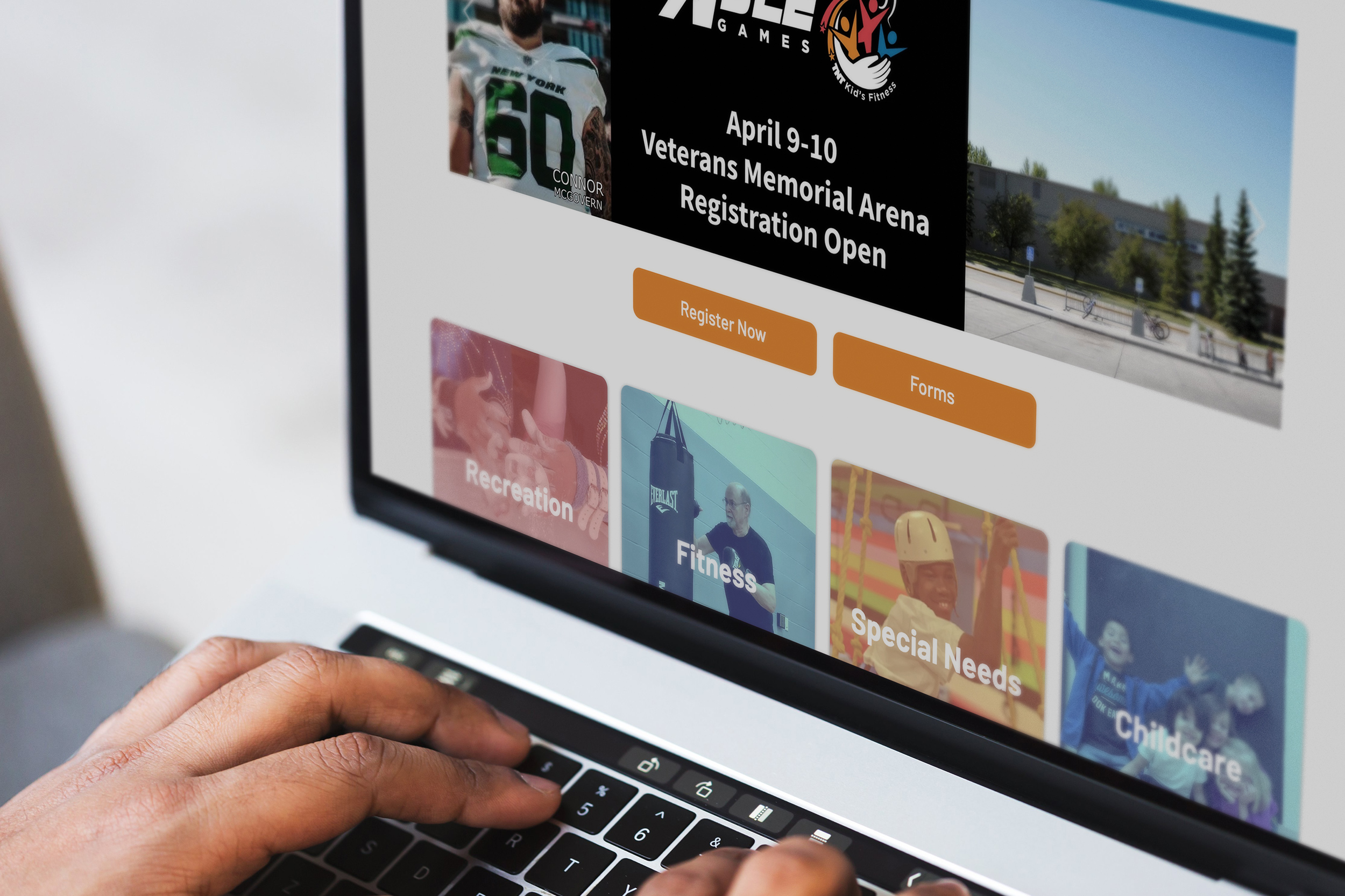
TNT Kid’s Fitness Website Redesign
February 25, 2022So you have a great product that you think everyone will want to buy, yet you’re not sure how exactly to sell it? Finding a cost-effective and efficient way to produce, distribute, and sell a product is challenging for any startup that is new to the commercial world. Unfortunately, many entrepreneurs too often fall into the trap of a “build it, and they will come” mentality where the startup focuses on building an incredible product but fails to consider how they will actually sell it.
There are many different outlets and ways to sell your product. Whether it be a digital platform or opening a brick-and-mortar storefront in your town, we’ll break down all of the options.
Types of selling
Before we dive into the different types of selling, we must first understand the two different categories they fall into, direct and indirect selling. Direct selling is where the consumer purchases the product or service directly from you instead of through a third-party service such as a distributor or reseller. This is typical in software and manufacturing companies who create custom products to meet their customer’s needs and do not mass produce their product.
On the other side is indirect selling, where you, as the product creator, will sell your products through a reseller or distributor like Amazon or Walmart, who will buy your product in bulk to sell it using their platform. While both of these are viable options, you’ll have to take into consideration what your product calls for and what you can handle in terms of distribution.
Now let’s check out the different types of selling.
Online Direct Selling
Online direct selling is selling products directly from your website, where customers pay you directly using their credit card or PayPal. Then you distribute the product yourself directly to the end-user. This is the most common practice for startups selling subscriptions such as SAAS products. This also includes startups selling a catalog of products such as a clothing brand. The benefit of this type is that you won’t have to pay a distribution or user fee like you may have to if you’re using an online platform. On the downside, you are responsible for all the supply chain management and distribution of the products, which may take extra time and energy.
Online Sales Management Platforms
Online sales platforms such as Amazon, eBay, Google Play, Apple App Store can be great tools to sell your products if you don’t want to worry about the distribution and are willing to pay a little to be on a larger platform. Selling on app stores is great as it allows for easier discovery for your app and gives you customization options for each platform. However, many of these platforms do take a small commission fee of anywhere from 10-30% off each sale, so be aware of the margins of using one of these platforms.
Inside Sales Reps
Inside selling through either telemarketing or web presentation is when salespeople within your company cold call or send messages to potential customers to get them to buy the product their company is selling. Their job is to contact customers all day and get sales or set up meetings over the phone. This can work for companies who are selling business to business with products such as software packages or hardware for businesses. The downside to this method is that it can be exhausting and challenging for the sales reps to land business. They can potentially cost your company a lot of money and not always have a positive ROI.
Outside Sales Reps
Field selling involves meeting with customers in person or going to trade shows and presenting the products face to face. The difference between inside sales reps and outside sales reps is that they travel to the buyer and are more engaged with the client, helping present the product in person or even helping install and teach the customer how to use the product.
Resellers and Distributors
An option to sell your product is to sell it in bulk to a distributor who will, in turn, be the reseller of the product. Because of this, you won’t have to do the hard work yourself. One significant benefit to this is that your product can make it nationwide without you having to sell in all markets, giving you the ability to expand your market.
Retail Selling
If you are looking to sell your products in your own physical or online store, retail selling is your best option. You will still be the seller of your product, but instead of worrying about shipping (besides the online sales), customers will come to you and into your store to buy your product(s) firsthand. This can be a challenge for startups and small businesses who don’t have a lot of upfront capital but can be great for companies who have a plethora of products and want to bring them to the mass market.
Wholesale Selling
Wholesale selling enables you to sell your product in bulk to a company such as Target or Best Buy and let them sell your product directly to consumers. This can be an effective method if you can’t build a sales team or don’t have the time to run your own sales plan. It allows you to leverage the wholesaler’s brand and market while focusing on building a great product.
Choosing the correct type of selling
For many startups, their product is the first thing on their minds. While development, production, and creation of the physical or digital product are important, none of those matter if you can’t actually sell it. The biggest thing to consider when deciding on how to sell your product is distribution; how do you, as the product owner, want to get your product to the end-user. These factors will help you choose if you want an online store or a physical one as well as how you will be distributing your product. If your product is completely digital, look at building an online shop. If you have a bulk of physical products, look at retail selling. Sales reps can work on almost any product but will cost money as they are employees. Being mindful of costs, supply chain, and product type will help you choose the best form of distribution and delivery for your startup’s big idea.
